AIM
8/15/19
5
−
4
−
52
Arrival Procedures
FIG 5
−
4
−
27
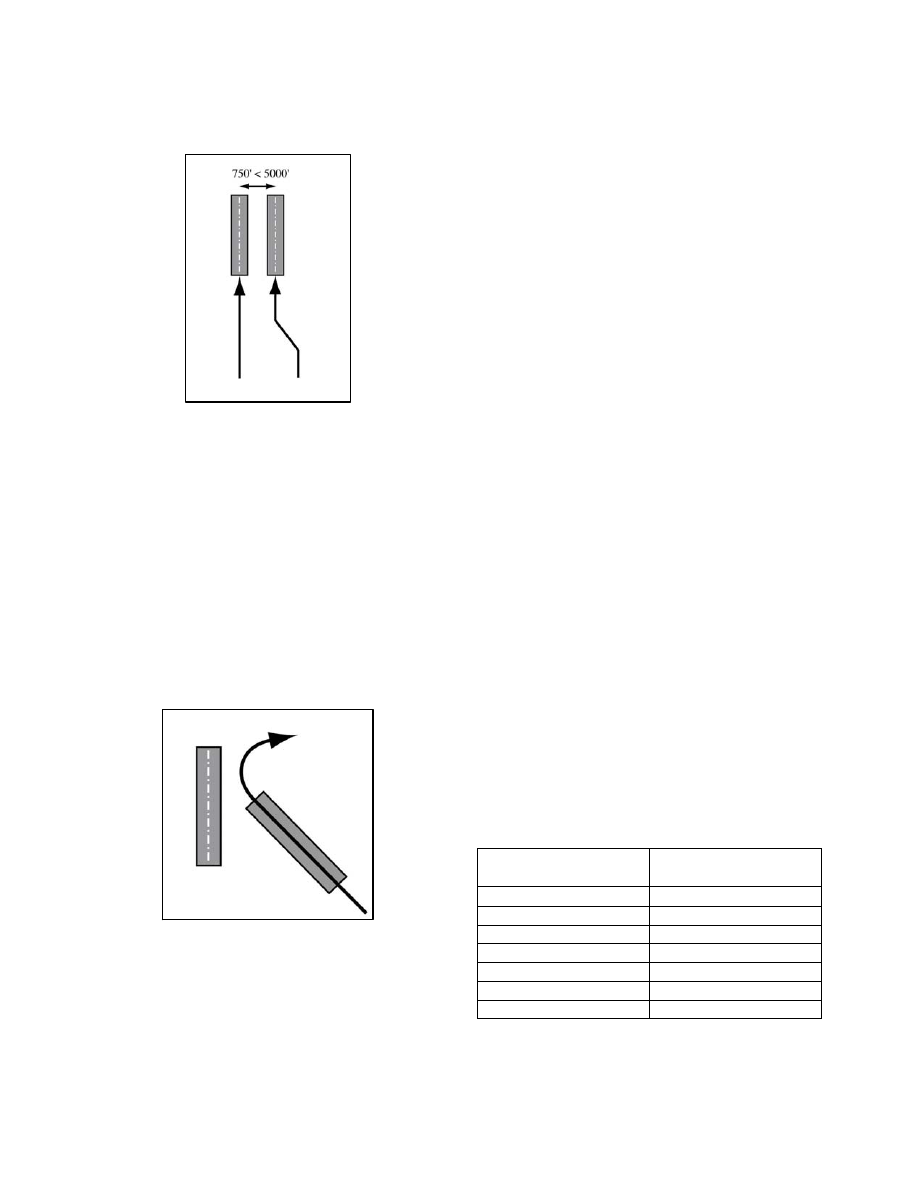
4. RNP Converging Runway Operations.
At
airports where runways converge, but may or may not
intersect, an RNP AR approach can provide a precise
curved missed approach path that conforms to aircraft
separation minimums for simultaneous operations
(See FIG 5
−
4
−
28). By flying this curved missed
approach path with high accuracy and containment
provided by RNP, dual runway operations may
continue to be used to lower ceiling and visibility
values than currently available. This type of
operation allows greater capacity at airports where it
can be applied.
FIG 5
−
4
−
28
5
−
4
−
19. Side
−
step Maneuver
a.
ATC may authorize a standard instrument
approach procedure which serves either one of
parallel runways that are separated by 1,200 feet or
less followed by a straight
−
in landing on the adjacent
runway.
b.
Aircraft that will execute a side
−
step maneuver
will be cleared for a specified approach procedure
and landing on the adjacent parallel runway.
Example, “cleared ILS runway 7 left approach,
side
−
step to runway 7 right.” Pilots are expected to
commence the side
−
step maneuver as soon as
possible after the runway or runway environment is
in sight. Compliance with minimum altitudes
associated with stepdown fixes is expected even after
the side
−
step maneuver is initiated.
NOTE
−
Side
−
step minima are flown to a Minimum Descent
Altitude (MDA) regardless of the approach authorized.
c.
Landing minimums to the adjacent runway will
be based on nonprecision criteria and therefore higher
than the precision minimums to the primary runway,
but will normally be lower than the published circling
minimums.
5
−
4
−
20. Approach and Landing Minimums
a. Landing Minimums.
The rules applicable to
landing minimums are contained in 14 CFR
Section 91.175. TBL 5
−
4
−
1 may be used to convert
RVR to ground or flight visibility. For converting
RVR values that fall between listed values, use the
next higher RVR value; do not interpolate. For
example, when converting 1800 RVR, use 2400 RVR
with the resultant visibility of
1
/
2
mile.
b. Obstacle Clearance.
Final approach obstacle
clearance is provided from the start of the final
segment to the runway or missed approach point,
whichever occurs last. Side
−
step obstacle protection
is provided by increasing the width of the final
approach obstacle clearance area.
TBL 5
−
4
−
1
RVR Value Conversions
RVR
Visibility
(statute miles)
1600
1
/
4
2400
1
/
2
3200
5
/
8
4000
3
/
4
4500
7
/
8
5000
1
6000
1
1
/
4