454
14 CFR Ch. I (1–1–19 Edition)
Pt. 25, App. M
T
ABLE
II.–HIRF E
NVIRONMENT
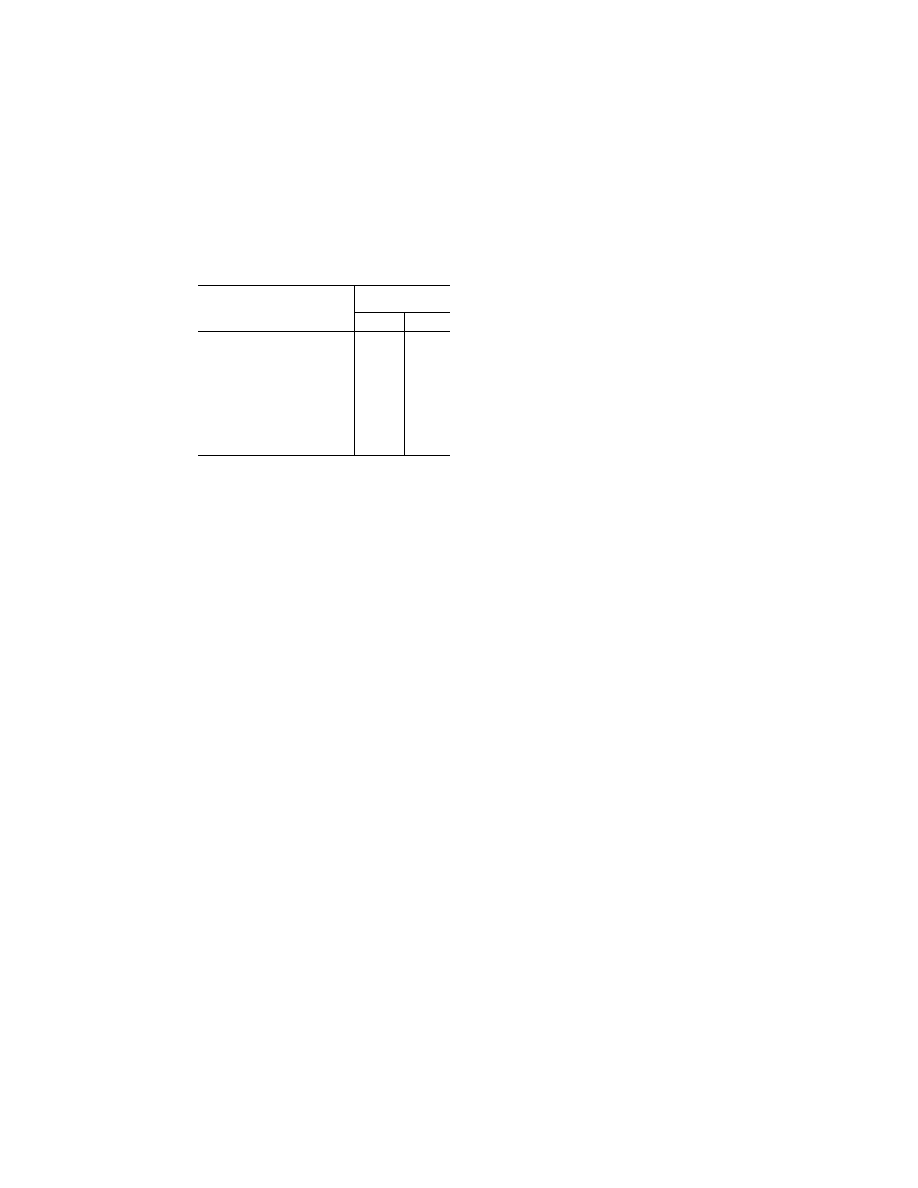
II—Continued
Frequency
Field strength
(volts/meter)
Peak Average
30 MHz–100 MHz .............................
10
10
100 MHz–200 MHz ...........................
30
10
200 MHz–400 MHz ...........................
10
10
400 MHz–1 GHz ................................
700
40
1 GHz–2 GHz ....................................
1,300
160
2 GHz–4 GHz ....................................
3,000
120
4 GHz–6 GHz ....................................
3,000
160
6 GHz–8 GHz ....................................
400
170
8 GHz–12 GHz ..................................
1,230
230
12 GHz–18 GHz ................................
730
190
18 GHz–40 GHz ................................
600
150
In this table, the higher field strength applies at the fre-
quency band edges.
(c)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 1.
(1) From 10
kilohertz (kHz) to 400 megahertz (MHz), use
conducted susceptibility tests with contin-
uous wave (CW) and 1 kHz square wave mod-
ulation with 90 percent depth or greater. The
conducted susceptibility current must start
at a minimum of 0.6 milliamperes (mA) at 10
kHz, increasing 20 decibels (dB) per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 30 mA at 500
kHz.
(2) From 500 kHz to 40 MHz, the conducted
susceptibility current must be at least 30
mA.
(3) From 40 MHz to 400 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests, starting at a minimum
of 30 mA at 40 MHz, decreasing 20 dB per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 3 mA at 400
MHz.
(4) From 100 MHz to 400 MHz, use radiated
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 20 volts
per meter (V/m) peak with CW and 1 kHz
square wave modulation with 90 percent
depth or greater.
(5) From 400 MHz to 8 gigahertz (GHz), use
radiated susceptibility tests at a minimum
of 150 V/m peak with pulse modulation of 4
percent duty cycle with a 1 kHz pulse repeti-
tion frequency. This signal must be switched
on and off at a rate of 1 Hz with a duty cycle
of 50 percent.
(d)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 2.
Equipment
HIRF test level 2 is HIRF environment II in
table II of this appendix reduced by accept-
able aircraft transfer function and attenu-
ation curves. Testing must cover the fre-
quency band of 10 kHz to 8 GHz.
(e)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 3.
(1) From 10
kHz to 400 MHz, use conducted susceptibility
tests, starting at a minimum of 0.15 mA at 10
kHz, increasing 20 dB per frequency decade
to a minimum of 7.5 mA at 500 kHz.
(2) From 500 kHz to 40 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 7.5 mA.
(3) From 40 MHz to 400 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests, starting at a minimum
of 7.5 mA at 40 MHz, decreasing 20 dB per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 0.75 mA at
400 MHz.
(4) From 100 MHz to 8 GHz, use radiated
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 5 V/m.
[Doc. No. FAA–2006–23657, 72 FR 44026, Aug. 6,
2007]
A
PPENDIX
M
TO
P
ART
25—F
UEL
T
ANK
S
YSTEM
F
LAMMABILITY
R
EDUCTION
M
EANS
M25.1
Fuel tank flammability exposure re-
quirements.
(a) The Fleet Average Flammability Expo-
sure of each fuel tank, as determined in ac-
cordance with Appendix N of this part, may
not exceed 3 percent of the Flammability Ex-
posure Evaluation Time (FEET), as defined
in Appendix N of this part. As a portion of
this 3 percent, if flammability reduction
means (FRM) are used, each of the following
time periods may not exceed 1.8 percent of
the FEET:
(1) When any FRM is operational but the
fuel tank is not inert and the tank is flam-
mable; and
(2) When any FRM is inoperative and the
tank is flammable.
(b) The Fleet Average Flammability Expo-
sure, as defined in Appendix N of this part, of
each fuel tank may not exceed 3 percent of
the portion of the FEET occurring during ei-
ther ground or takeoff/climb phases of flight
during warm days. The analysis must con-
sider the following conditions.
(1) The analysis must use the subset of
those flights that begin with a sea level
ground ambient temperature of 80
°
F (stand-
ard day plus 21
°
F atmosphere) or above,
from the flammability exposure analysis
done for overall performance.
(2) For the ground and takeoff/climb phases
of flight, the average flammability exposure
must be calculated by dividing the time dur-
ing the specific flight phase the fuel tank is
flammable by the total time of the specific
flight phase.
(3) Compliance with this paragraph may be
shown using only those flights for which the
airplane is dispatched with the flammability
reduction means operational.
M25.2
Showing compliance.
(a) The applicant must provide data from
analysis, ground testing, and flight testing,
or any combination of these, that:
(1) Validate the parameters used in the
analysis required by paragraph M25.1 of this
appendix;
(2) Substantiate that the FRM is effective
at limiting flammability exposure in all
compartments of each tank for which the
FRM is used to show compliance with para-
graph M25.1 of this appendix; and
(3) Describe the circumstances under which
the FRM would not be operated during each
phase of flight.
(b) The applicant must validate that the
FRM meets the requirements of paragraph
VerDate Sep<11>2014
12:50 Apr 30, 2019
Jkt 247046
PO 00000
Frm 00464
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8002
Y:\SGML\247046.XXX
247046
spaschal on DSK3GDR082PROD with CFR