571
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
Pt. 29
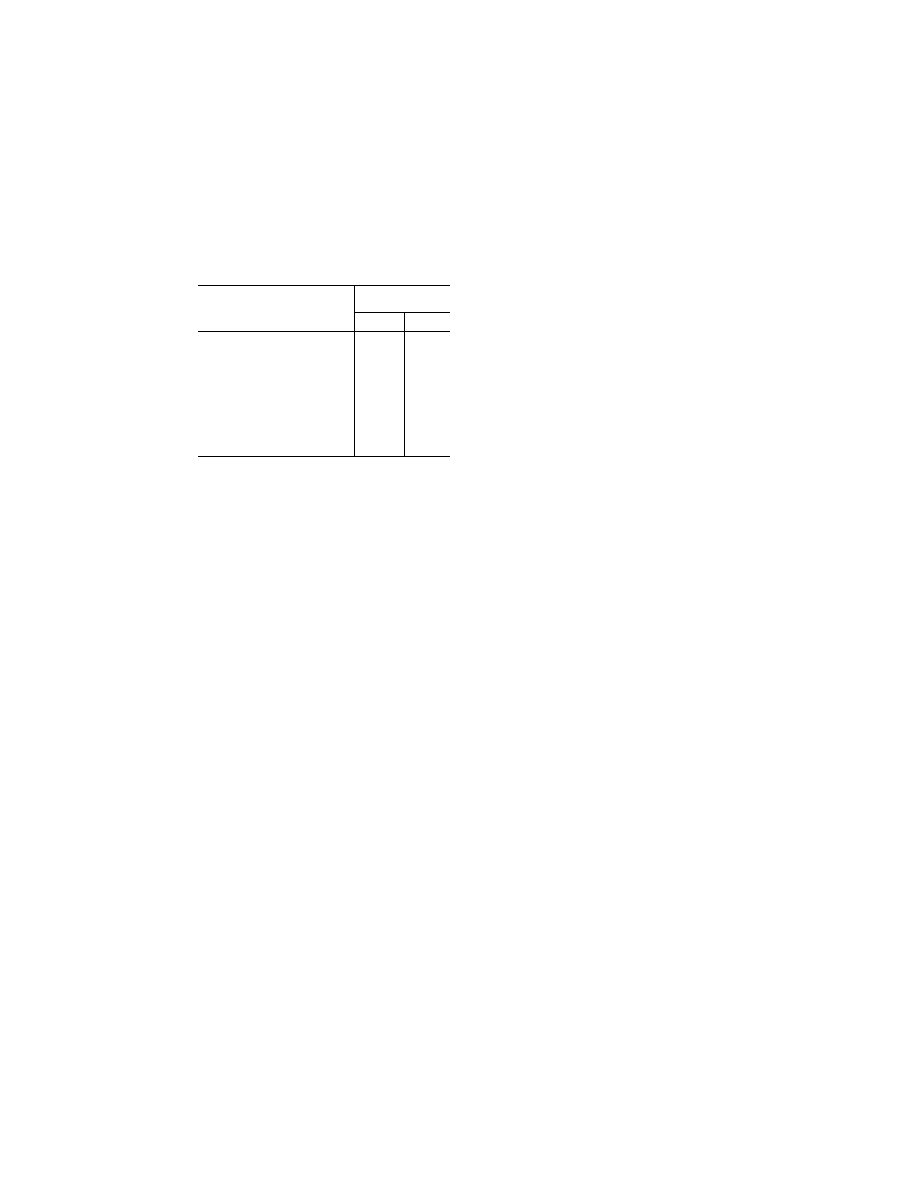
T
ABLE
III.—HIRF E
NVIRONMENT
III
Frequency
Field strength
(volts/meter)
Peak Average
10 kHz–100 kHz ................................
150
150
100 kHz–400 MHz .............................
200
200
400 MHz–700 MHz ...........................
730
200
700 MHz–1 GHz ................................
1,400
240
1 GHz–2 GHz ....................................
5,000
250
2 GHz–4 GHz ....................................
6,000
490
4 GHz–6 GHz ....................................
7,200
400
6 GHz–8 GHz ....................................
1,100
170
8 GHz–12 GHz ..................................
5,000
330
12 GHz–18 GHz ................................
2,000
330
18 GHz–40 GHz ................................
1,000
420
In this table, the higher field strength applies at the fre-
quency band edges.
(d)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 1.
(1) From 10
kilohertz (kHz) to 400 megahertz (MHz), use
conducted susceptibility tests with contin-
uous wave (CW) and 1 kHz square wave mod-
ulation with 90 percent depth or greater. The
conducted susceptibility current must start
at a minimum of 0.6 milliamperes (mA) at 10
kHz, increasing 20 decibels (dB) per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 30 mA at 500
kHz.
(2) From 500 kHz to 40 MHz, the conducted
susceptibility current must be at least 30
mA.
(3) From 40 MHz to 400 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests, starting at a minimum
of 30 mA at 40 MHz, decreasing 20 dB per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 3 mA at 400
MHz.
(4) From 100 MHz to 400 MHz, use radiated
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 20 volts
per meter (V/m) peak with CW and 1 kHz
square wave modulation with 90 percent
depth or greater.
(5) From 400 MHz to 8 gigahertz (GHz), use
radiated susceptibility tests at a minimum
of 150 V/m peak with pulse modulation of 4
percent duty cycle with a 1 kHz pulse repeti-
tion frequency. This signal must be switched
on and off at a rate of 1 Hz with a duty cycle
of 50 percent.
(e)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 2.
Equipment
HIRF test level 2 is HIRF environment II in
table II of this appendix reduced by accept-
able aircraft transfer function and attenu-
ation curves. Testing must cover the fre-
quency band of 10 kHz to 8 GHz.
(f)
Equipment HIRF Test Level 3.
(1) From 10
kHz to 400 MHz, use conducted susceptibility
tests, starting at a minimum of 0.15 mA at 10
kHz, increasing 20 dB per frequency decade
to a minimum of 7.5 mA at 500 kHz.
(2) From 500 kHz to 40 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 7.5 mA.
(3) From 40 MHz to 400 MHz, use conducted
susceptibility tests, starting at a minimum
of 7.5 mA at 40 MHz, decreasing 20 dB per fre-
quency decade to a minimum of 0.75 mA at
400 MHz.
(4) From 100 MHz to 8 GHz, use radiated
susceptibility tests at a minimum of 5 V/m.
[Doc. No. FAA–2006–23657, 72 FR 44027, Aug. 6,
2007]
PART 29—AIRWORTHINESS STAND-
ARDS: TRANSPORT CATEGORY
ROTORCRAFT
Subpart A—General
Sec.
29.1
Applicability.
29.2
Special retroactive requirements.
Subpart B—Flight
G
ENERAL
29.21
Proof of compliance.
29.25
Weight limits.
29.27
Center of gravity limits.
29.29
Empty weight and corresponding cen-
ter of gravity.
29.31
Removable ballast.
29.33
Main rotor speed and pitch limits.
P
ERFORMANCE
29.45
General.
29.49
Performance at minimum operating
speed.
29.51
Takeoff data: general.
29.53
Takeoff: Category A.
29.55
Takeoff decision point (TDP): Cat-
egory A.
29.59
Takeoff path: Category A.
29.60
Elevated heliport takeoff path: Cat-
egory A.
29.61
Takeoff distance: Category A.
29.62
Rejected takeoff: Category A.
29.63
Takeoff: Category B.
29.64
Climb: General.
29.65
Climb: All engines operating.
29.67
Climb: One engine inoperative (OEI).
29.71
Helicopter angle of glide: Category B.
29.75
Landing: General.
29.77
Landing Decision Point (LDP): Cat-
egory A.
29.79
Landing: Category A.
29.81
Landing distance: Category A.
29.83
Landing: Category B.
29.85
Balked landing: Category A.
29.87
Height-velocity envelope.
F
LIGHT
C
HARACTERISTICS
29.141
General.
29.143
Controllability and maneuverability.
29.151
Flight controls.
29.161
Trim control.
29.171
Stability: general.
29.173
Static longitudinal stability.
29.175
Demonstration of static longitudinal
stability.
29.177
Static directional stability.
29.181
Dynamic stability: Category A rotor-
craft.
VerDate Sep<11>2014
12:50 Apr 30, 2019
Jkt 247046
PO 00000
Frm 00581
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Y:\SGML\247046.XXX
247046
spaschal on DSK3GDR082PROD with CFR