643
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
Pt. 63, App. B
for a ground training course for flight navi-
gators:
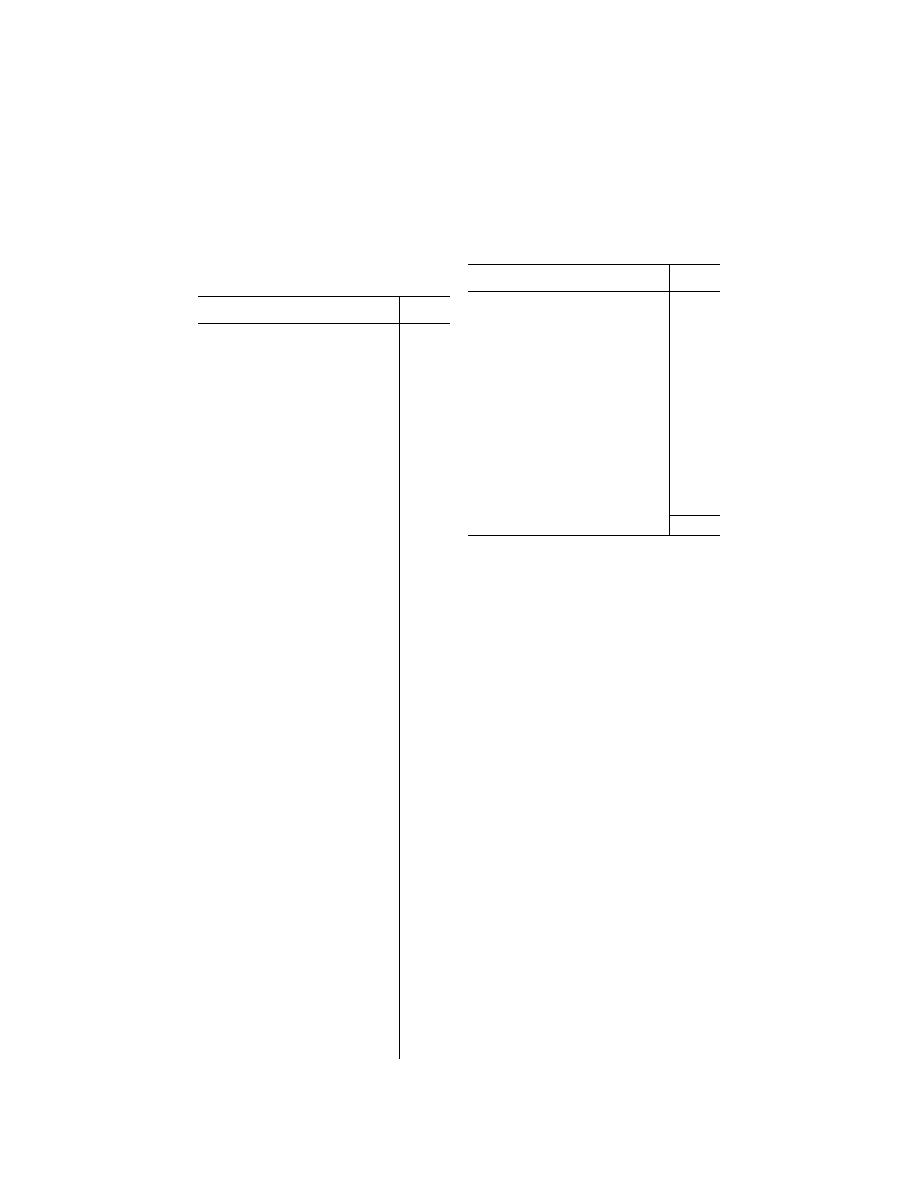
Subject
Classroom
hours
Federal Aviation Administration ...........................
5
To include Parts 63, 91, and 121 of this
chapter.
Meteorology .........................................................
40
To include:
Basic weather principles.
Temperature.
Pressure.
Winds.
Moisture in the atmosphere.
Stability.
Clouds.
Hazards.
Air masses.
Front weather.
Fog.
Thunderstorms.
Icing.
World weather and climate.
Weather maps and weather reports.
Forecasting.
International Morse code:
Ability to receive code groups of letters and
numerals at a speed of eight words per
minute
Navigation instruments (exclusive of radio and
radar) ................................................................
20
To include:
Compasses.
Pressure altimeters.
Airspeed indicators.
Driftmeters.
Bearing indicators.
Aircraft octants.
Instrument calibration and alignment.
Charts and pilotage .............................................
15
To include:
Chart projections.
Chart symbols.
Principles of pilotage.
Dead reckoning ...................................................
30
To include:
Air plot.
Ground plot.
Calculation of ETA.
Vector analysis.
Use of computer.
Search.
Absolute altimeter with:
Applications .........................................................
15
To include:
Principles of construction.
Operating instructions.
Use of Bellamy’s formula.
Flight planning with single drift correc-
tion.
Radio and long-range navigational aids ..............
35
To include:
Principles of radio transmission and re-
ception.
Radio aids to navigation.
Government publications.
Airborne D/F equipment.
Errors of radio bearings.
Quadrantal correction.
Plotting radio bearings.
ICAO Q code for direction finding.
Celestial navigation .............................................
150
Subject
Classroom
hours
To include:
The solar system.
The celestial sphere.
The astronomical triangle.
Theory of lines of position.
Use of the Air Almanac.
Time and its applications.
Navigation tables.
Precomputation.
Celestial line of position approach.
Star identification.
Corrections to celestial observations.
Flight planning and cruise control .......................
25
To include:
The flight plan.
Fuel consumption charts.
Methods of cruise control.
Flight progress chart.
Point-of-no-return.
Equitime point.
Long-range flight problems ..................................
15
Total (exclusive of final examinations) ..
350
(3)
Flight course outline.
(i) A minimum of
150 hours of supervised flight training shall
be given, of which at least 50 hours of flight
training must be given at night, and celes-
tial navigation must be used during flights
which total at least 125 hours.
(ii) A maximum of 50 hours of the required
flight training may be obtained in accept-
able types of synthetic flight navigator
training devices.
(iii) Flights should be at least four hours in
length and should be conducted off civil air-
ways. Some training on long-range flights is
desirable, but is not required. There is no
limit to the number of students that may be
trained on one flight, but at least one
astrodrome or one periscopic sextant mount-
ing must be provided for each group of four
students.
(iv) Training must be given in dead reck-
oning, pilotage, radio navigation, celestial
navigation, and the use of the absolute al-
timeter.
(b)
Equipment.
(1) Classroom equipment
shall include one table at least 24
″ ×
32
″
in di-
mensions for each student.
(2) Aircraft suitable for the flight training
must be available to the approved course op-
erator to insure that the flight training may
be completed without undue delay.
The approved course operator may contract
or obtain written agreements with aircraft
operators for the use of suitable aircraft. A
copy of the contract or written agreement
with an aircraft operator shall be attached
to each of the three copies of the course out-
line submitted for approval. In all cases, the
approved course operator is responsible for
the nature and quality of instruction given
during flight.
(c)
Instructors.
(1) Sufficient classroom in-
structors must be available to prevent an ex-
cessive ratio of students to instructors. Any
VerDate Sep<11>2014
16:30 Jun 25, 2019
Jkt 247047
PO 00000
Frm 00653
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8002
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
kpayne on VMOFRWIN702 with $$_JOB