AIM
4/3/14
10−1−4
Helicopter IFR Operations
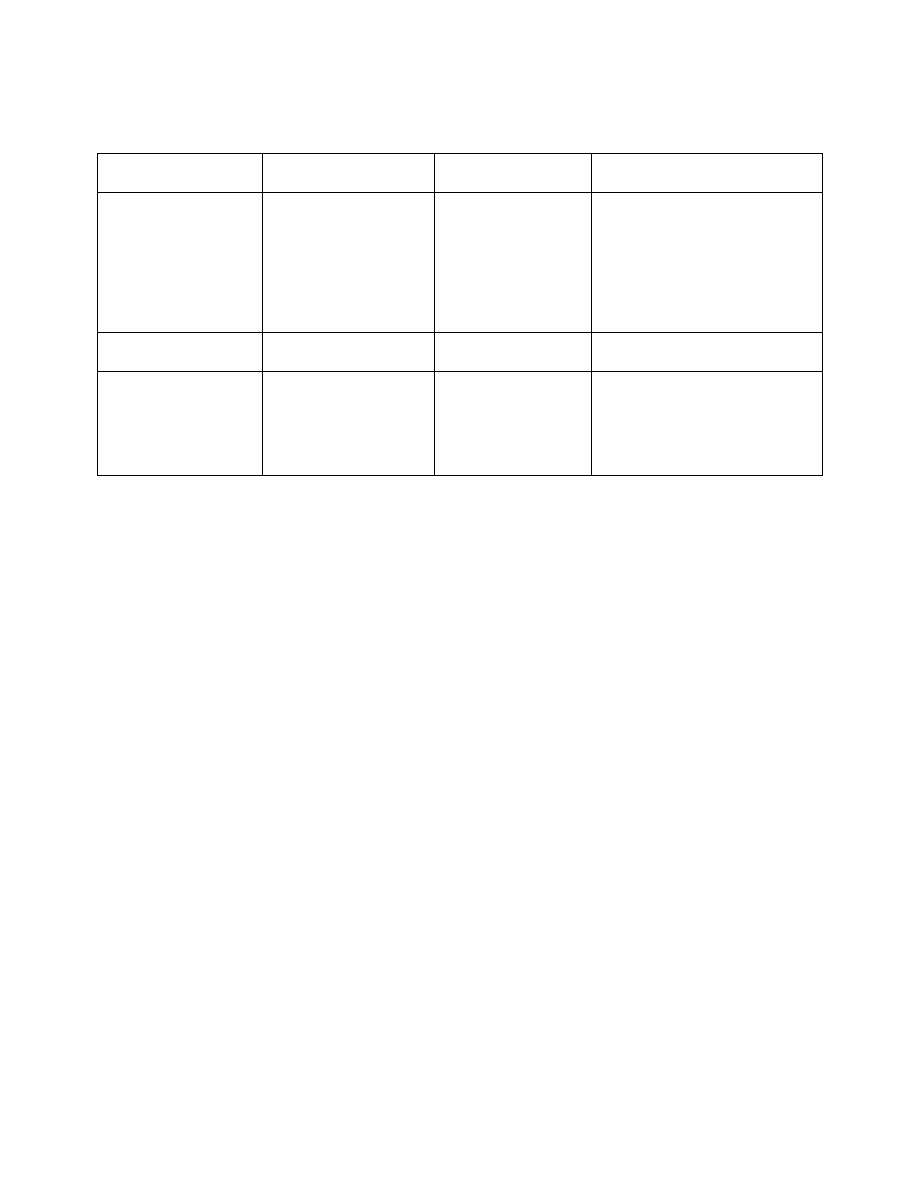
TBL 10
−1−1
Helicopter Use of Standard Instrument Approach Procedures
Procedure
Helicopter Visibility
Minima
Helicopter MDA/DA
Maximum Speed Limitations
Conventional
(non
−Copter)
The greater of: one half
the Category A visibility
minima,
1
/
4
statute mile
visibility, or 1200 RVR
As published for
Category A
The helicopter may initiate the final
approach segment at speeds up to
the upper limit of the highest
Approach Category authorized by
the procedure, but must be slowed
to no more than 90 KIAS at the
MAP in order to apply the visibility
reduction.
Copter Procedure
As published
As published
90 KIAS when on a published
route/track.
GPS Copter Procedure
As published
As published
90 KIAS when on a published route
or track, EXCEPT 70 KIAS when
on the final approach or missed
approach segment and, if annotated,
in holding. Military procedures are
limited to 90 KIAS for all segments.
NOTE
−
Several factors effect the ability of the pilot to acquire and
maintain the visual references specified in 14 CFR
Section 91.175(c), even in cases where the flight visibility
may be at the minimum derived by TBL 10
factors include, but are not limited to:
1. Cockpit cutoff angle (the angle at which the cockpit or
other airframe structure limits downward visibility below
the horizon).
2. Combinations of high MDA/DH and low visibility
minimum, such as a conventional nonprecision approach
with a reduced helicopter visibility minima (per 14 CFR
Section 97.3).
3. Type, configuration, and intensity of approach and
runway lighting systems.
4. Type of obscuring phenomenon and/or windshield
contamination.