AIM
4/3/14
4−5−15
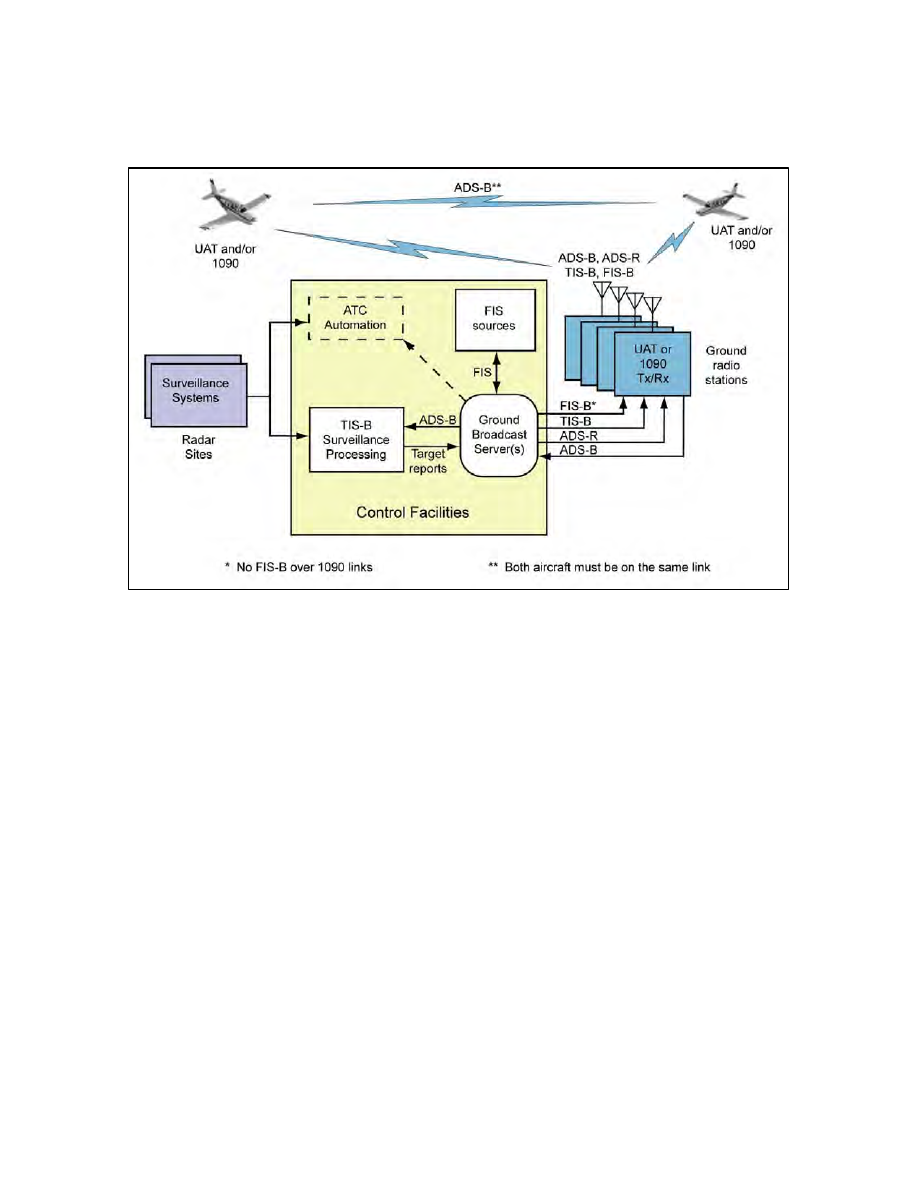
Surveillance Systems
FIG 4
−5−7
ADS
−B, TIS−B, and FIS−B:
Broadcast Services Architecture
3.
ADS B avionics can have the ability to both
transmit and receive information. The transmission
of ADS−B information from an aircraft is known as
ADS−B Out. The receipt of ADS−B information by
an aircraft is known as ADS−B In. On January 1,
2020, all aircraft operating within the airspace
defined in 14 CFR part 91, § 91.225 will be required
to transmit the information defined in § 91.227
using ADS−B Out avionics.
4.
In general, operators flying at 18,000 feet and
above will require equipment which uses 1090 ES.
Those that do not fly above 18,000 may use either
UAT or 1090ES equipment. (Refer to 14 CFR 91.225
and 91.227.) While the regulation will not require it,
operators equipped with ADS−B In will realize
additional benefits from ADS−B broadcast services:
Traffic Information Service – Broadcast (TIS−B)
(paragraph 4−5−8) and Flight Information Service −
Broadcast (FIS−B) (paragraph 4−5−9).
b. ADS
−B Certification and Performance
Requirements
ADS−B equipment may be certified as a surveillance
source for air traffic separation services using
ADS−B Out. ADS−B equipment may also be
certified for use with ADS−B In advisory services
that enable appropriately equipped aircraft to
display traffic and flight information. Refer to the
aircraft’s flight manual supplement or Pilot
Operating Handbook for the capabilities of a specific
aircraft installation.
c. ADS
−B Capabilities
1.
ADS−B enables improved surveillance ser-
vices, both air−to−air and air−to−ground, especially
in areas where radar is ineffective due to terrain or
where it is impractical or cost prohibitive. Initial NAS
applications of air−to−air ADS−B are for “advisory”
use only, enhancing a pilot’s visual acquisition of
other nearby equipped aircraft either when airborne
or on the airport surface. Additionally, ADS−B will
enable ATC and fleet operators to monitor aircraft
throughout the available ground station coverage
area.
2.
ADS−B avionics typically allow pilots to
enter the aircraft’s call sign and Air Traffic Control
(ATC)−assigned transponder code, which will be
transmitted to other aircraft and ground receivers.
Pilots are cautioned to use care when selecting and