AIM
4/3/14
1−2−4
Area Navigation (RNAV) and Required Navigation Performance (RNP)
1
−
2
−
2. Required Navigation Performance
(RNP)
a. General.
RNP is RNAV with on−board
navigation monitoring and alerting, RNP is also a
statement of navigation performance necessary for
operation within a defined airspace. A critical
component of RNP is the ability of the aircraft
navigation system to monitor its achieved navigation
performance, and to identify for the pilot whether the
operational requirement is, or is not being met during
an operation
. This on−board performance monitor-
ing and alerting capability therefore allows a lessened
reliance on air traffic control intervention (via radar
monitoring, automatic dependent surveillance
(ADS), multilateration, communications), and/or
route separation to achieve the overall safety of the
operation. RNP capability of the aircraft is a major
component in determining the separation criteria to
ensure that the overall containment of the operation
is met.
The RNP capability of an aircraft will vary depending
upon the aircraft equipment and the navigation
infrastructure. For example, an aircraft may be
equipped and certified for RNP 1.0, but may not be
capable of RNP 1.0 operations due to limited navaid
coverage.
b. RNP Operations.
1. RNP Levels.
An RNP “level” or “type” is
applicable to a selected airspace, route, or procedure.
As defined in the Pilot/Controller Glossary, the RNP
Level or Type is a value typically expressed as a
distance in nautical miles from the intended
centerline of a procedure, route, or path. RNP
applications also account for potential errors at some
multiple of RNP level (e.g., twice the RNP level).
(a) Standard RNP Levels.
U.S. standard
values supporting typical RNP airspace are as
specified in TBL 1−2−1 below. Other RNP levels as
identified by ICAO, other states and the FAA may
also be used.
(b) Application of Standard RNP Levels.
U.S. standard levels of RNP typically used for
various routes and procedures supporting RNAV
operations may be based on use of a specific
navigational system or sensor such as GPS, or on
multi−sensor RNAV systems having suitable perfor-
mance.
(c) Depiction of Standard RNP Levels.
The
applicable RNP level will be depicted on affected
charts and procedures.
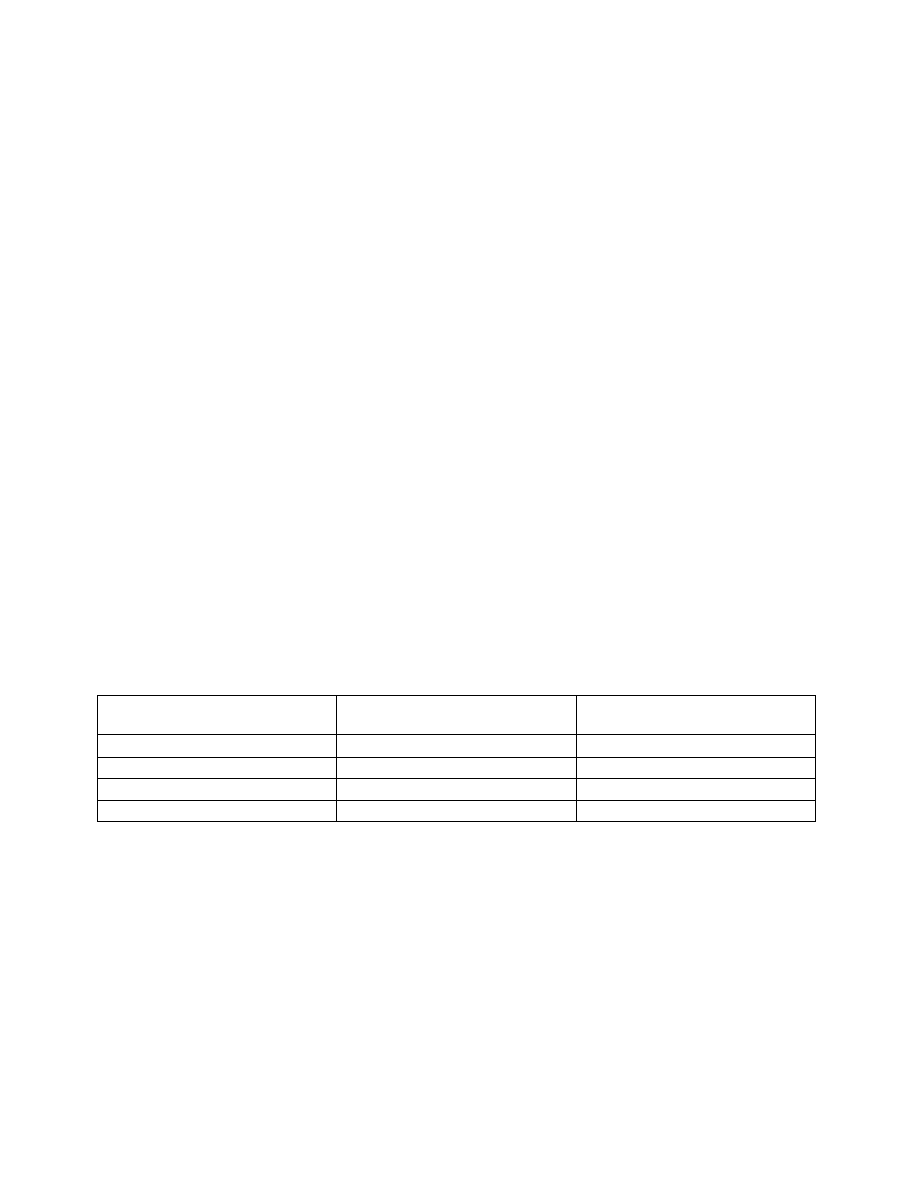
TBL 1
−2−1
U.S. Standard RNP Levels
RNP Level
Typical Application
Primary Route Width (NM)
−
Centerline to Boundary
0.1 to 1.0
RNP AR Approach Segments
0.1 to 1.0
0.3 to 1.0
RNP Approach Segments
0.3 to 1.0
1
Terminal and En Route
1.0
2
En Route
2.0
NOTE
−
1. The “performance” of navigation in RNP refers not only to the level of accuracy of a particular sensor or aircraft
navigation system, but also to the degree of precision with which the aircraft will be flown.
2. Specific required flight procedures may vary for different RNP levels.